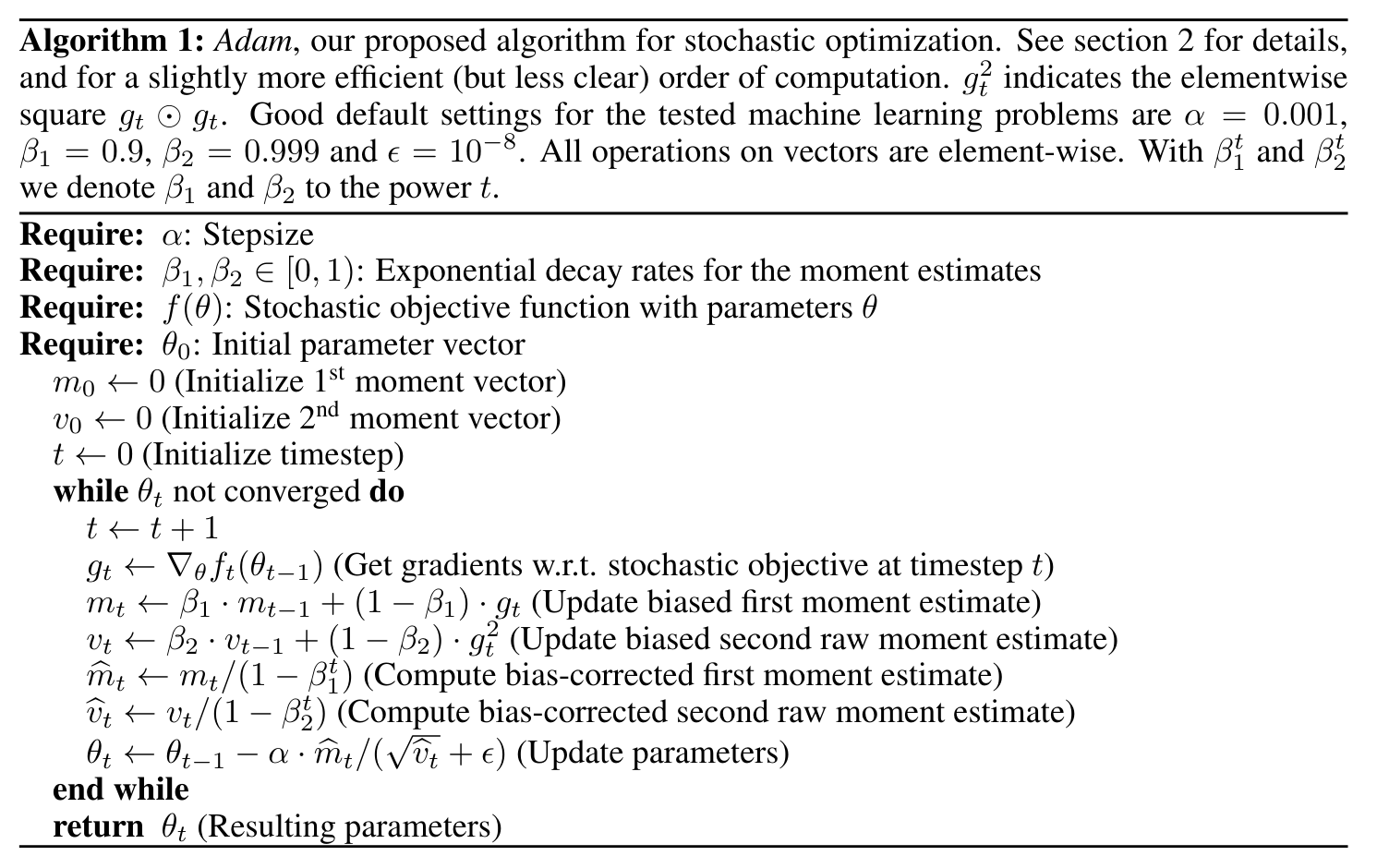
12.1. Adam
Our implementation API:
- class fhez.nn.optimiser.adam.Adam(alpha: float = 0.001, beta_1: float = 0.9, beta_2: float = 0.999, epsilon: float = 1e-08)
Adaptive moment optimiser abstraction.
Sources:
- property alpha
Get learning rate hyperparameter.
- Returns
alpha \(\alpha\), defaults to \(0.001\)
- Return type
float
- property beta_1
Get first order moment exponential decay rate.
- Returns
beta_1 \(\beta_1\), defaults to \(0.9\)
- Return type
float
- property beta_2
Get second order moment exponential decay rate.
- Returns
beta_2 \(\beta_2\), defaults to \(0.999\)
- Return type
float
- property cache
Cache of iteration specific values.
This cache is a dictionary of keys (the parameter name) and values (the parameter specific variables). For example in this cache you can expect to get the previous iterations moment, and number of iterations.
- property epsilon
Get epsilon.
- Returns
epsilon \(\epsilon\) (not \(\varepsilon\)), defaults to \(1e^{-8}\)
- Return type
float
- momentum(gradient: float, param_name: str, ord: int = 1)
Calculate momentum, of a single parameter-category/ name.
This function can calculate either 1st order momentum or 2nd order momentum (rmsprop) since they are both almost identical.
where moment is 1 (I.E first order):
current moment \(m_t = \beta_1 * m_{t-1} + (1-\beta_1) * g_t\)
decayed moment \(\hat{m_t} = \frac{m_t}{1 – \beta_1^t}\)
where moment is 2 (I.E second order/ RMSprop):
current moment \(v_t = \beta_2 * v_{t-1} + (1-\beta_2) * g_t^2\)
decayed moment \(\hat{v_t} = \frac{v_t}{1 – \beta_2^t}\)
Steps taken:
retrieve previous momentum from cache dictionary using key (param_name) and number of iterations
calculate current momentum using previous momentum:
Save current momentum into cache dictionary using key
calculate current momentum correction/ decay:
return decayed momentum
- Parameters
gradient (float) – gradient at current timestep, usually minibatch
param_name (str) – key used to look up parameters in m_t dictionary
ord (int) – the order of momentum to calculate defaults to 1
- Returns
\(\hat{m_t}\) corrected/ averaged momentum of order ord
- Return type
float
- Example
Adam().momentum(gradient=100, param_name=”w”, ord=1)
- optimise(parms: dict, grads: dict)
Update given params based on gradients using Adam.
Params and grads keys are expected to be x and dfdx respectiveley. They should match although the x in this case should re replaced by any uniquely identifying string sequence.
- Parameters
parms (dict[str, float]) – Dictionary of keys (param name), values (param value)
grads (dict[str, float]) – Dictionary of keys (param name), values (param gradient)
- Returns
Dictionary of keys (param name), values (proposed new value)
- Return type
dict[str, float]
- Example
Adam().optimise({“b”: 1},{“dfdb”: 200})
- rmsprop(gradient: float, param_name: str)
Get second order momentum.
- property schema
Get Marshmallow schema representation of this class.
Marshmallow schemas allow for easy and trustworthy serialisation and deserialisation of arbitrary objects either to inbulit types or json formats. This is an inherited member of the abstract class Serialise.
Note
Anything not listed here will inevitably be lost, ensure anything important is identified and expressley stated its type and structure.